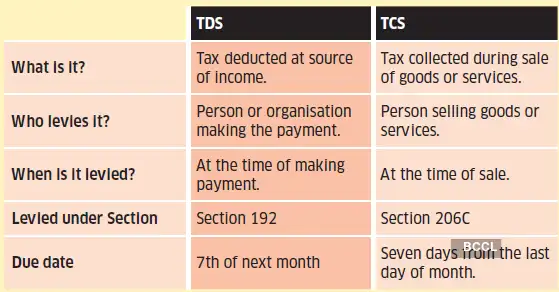
Tax deducted at source (TDS) and tax collected at source (TCS) are two forms of indirect tax collection. Here, tax is levied at the source of income or transaction if it exceeds a certain limit. Failure to deduct or collect this tax can lead to penalties and interest.
Here’s how the two types of indirect taxes differ.
What is TDS?
This tax is deducted at the source of one’s income. It is done by the person, organisation or employer making the payment, or providing salary or income. The person cutting the tax deposits it with the government.
The person who receives the income after deduction is called ‘deductee’, while the person cutting the tax is ‘deductor’. The rate at which the tax is deducted varies for different income options, such as salary, rent, interest income, commission or brokerage, purchase of property, professional fees, etc.
For instance, if you are paying a rent of Rs.60,000 a month, which exceeds the threshold of Rs.50,000, you will have to deduct tax at 10% before paying it to the landlord. So, you will deduct Rs.6,000 and pay Rs.54,000 to the landlord as rent.
What is TCS?
This tax is collected by the person selling certain goods or services, from the buyer, under Section 206C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The seller then deposits this tax with the government. Some of these goods include liquor, forest produce, minerals, purchase of vehicles, foreign remittances, among others, and the rate varies depending on the goods or services.
For instance, if you are travelling abroad and the tour package is Rs.12 lakh, above the threshold of Rs.10 lakh, then the tour operator will collect 20% tax on the excess amount. Hence, you will pay a tax of Rs.40,000.
Difference between TDS & TCS